Small Scale Industries

Muhammed Shameem PV
2005 IC
Small Scale Industries -A Collective and Distributed Approach
Unemployment is one of the crucial challenges that Kerala is facing in these pandemic days. Some of the major hurdles in generating jobs are lack of finance to start big industries, unavailability of vacant land for building huge infrastructure, and environmental impacts due to the big industries.
In this era of globalization, foreign and private investments are projected as the only solution for generating finance and reducing unemployment. But it will be a solution without addressing the issues like unavailability of vacant land and environmental impacts. Moreover, it will be dangerous to open our land, water and natural resources to international corporates with agreements based only on their profit shares. Most importantly, they will never be interested in assuring the labour rights of our workforce and preserving our environment.
Here, we need alternative approaches which could assure generation of more jobs, optimal use of land, minimal impact on our environment and protection of the rights of our people.
Small scale and medium scale industries are the possible solutions for this crisis. However, the small and medium scale industries face a variety of challenges in making sustainable business. Lack of expertise, technology upgradation, research, marketing, quality assurance, sales channels etc are a few of them. This document proposes a new model which could transform the informal small-scale industries into a more formal and sustainable business through a collective and distributed approach while ensuring people’s participation and ownership.
Challenges for Small Scale Industries.
Most of the small-scale industries face a variety of challenges and issues. following are few among them.
⦁ Lack of a brand name. It is difficult to sell products without a brand name. However, it is not affordable for individual units to brand their products.
⦁ Lack of quality guidelines and proper quality checking mechanisms.
⦁ Lack of public’s confidence about the quality of products.
⦁ Lack of state of art technology, research, and timely upgrading of technology of product and production. The small units can’t afford these costs.
⦁ Lack of centralized supply chain mechanisms and high cost of raw materials. Units need to buy the raw material individually. Bulk purchase of raw materials can reduce the cost of raw materials.
⦁ Improper marketing and sales channels. Each small unit individually manages their sales and marketing. A single brand umbrella for similar products may improve this.
⦁ Lack of expertise and guidance in management, technology, marketing etc.
⦁ Lack of expertise and guidance in finding the required finance.
In most cases these small units do not have technical and managerial expertise to solve these issues and take their business to the next level.
In order to sustain as a business in long term, the following factors seems to be very important.
⦁ Proper organizational structure.
⦁ Storage and Processing facility.
⦁ Quality assurance mechanism.
⦁ Dedicated Sales and Marketing teams.
⦁ Research and Innovation.
⦁ Adequate financial support.
There should be short term and long-term action plans to progress and realise the above mentioned aspects and establish as a sustainable business in the long run. The proposed approach can bring together these small units under a single umbrella to surmount the challenges and take their business to the next level.
A successful model will help to bring other small-scale industries also to the same approach.
Collective and Distributed Approach.
The collective and distributed approach brings together the best practices from co-operative and corporate worlds. Similar to the co-operative model, individual business units will be owned by the members while it will follow the corporate practices to ensure efficiency, quality, innovation and sustainability.
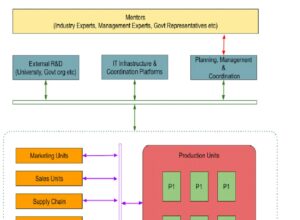
The collective and distributed business approach is based on a set of small and independent business units. Each unit will be financially independent but mutually dependent in the business workflow. Units will be individually financed. However, Some of the units can be collectively financed by all the units based on the business work flow and financial needs. Each unit will have independent targets based on the type of unit. Units can be geographically distributed based on business requirements. The following are a few types of units in this business model.
⦁ Production units.
⦁ Supply chain units.
⦁ Quality assurance units
⦁ Research units.
⦁ Sales units.
⦁ Marketing units.
⦁ IT Infrastructure and Coordination platforms unit.
⦁ Planning, Management and Coordination units.
⦁ Mentoring Unit.
Each type of unit serves different purposes in the business workflow. Some of the units can be removed or new types of units can be added based on the business needs of a particular industry or product.
Mentoring Unit
Mentoring unit is responsible for guiding and mentoring all other units on various aspects of the business. The following are the major roles and responsibilities of the Mentoring unit. Industrial experts, Management experts, government representatives etc can be part of this unit.
⦁ Responsible for identifying new business opportunities suitable for this model.
⦁ Selecting an existing business suitable for this model.
⦁ Responsible for guiding and advising the units on selecting the technology, branding, marketing, sales and all other aspects of the business.
⦁ Responsible acting as a bridge between the research requirements of the units and the public agencies (Universities, Government Industrial research institutes etc.).
⦁ Responsible for ensuring the environmental aspects.
⦁ Responsible for advising the production units and other units on how they can get necessary funds through loans and other government schemes.
Production Units
Production Units are responsible for the actual production. Instead of concentrating the production units in a single big factory which requires large vacant land and infrastructure, here the production units can be small units which could accommodate up to 5-15 members.
Each unit will be individually financed, and the funding needs to be realised though loans and government schemes. Every member in the unit should equally invest. This will make every member an owner of the business and it will create a complete ownership attitude towards the business which will help everyone to put their best efforts for the success of each unit.
The mentoring unit should ensure that the most efficient technologies suitable for each unit is selected.
The mentoring and Coordination units need to plan and decide the product and part of the product from each unit. Availability of raw material, market, ease of transportation and other factors can decide the geographical location of each unit and the distance between each unit.
Supply Chain Management Units
The following are the responsibilities of this unit.
⦁ These units are responsible for providing the best quality raw materials to all production units.
⦁ Responsible for ensuring the best possible rates. They can do bulk purchase and ensure minimum raw material cost.
⦁ Ensures timely intervention meeting the demand and supply.
Quality Assurance Units
The Quality assurance team is responsible for ensuring end to end quality. The following are the major responsibilities.
⦁ Preparing quality criteria expected from each unit and communicating the same with them.
⦁ Ensuring the quality of deliverables from different types of units. Eg: Ensure the quality of final product from production units, quality of raw materials provided by supply chain units.
⦁ Quality team can reject or accept a particular deliverable from any unit based on quality criteria.
⦁ It is the responsibility of each unit to make deliverables which meets the criteria
communicated by the quality unit.
⦁ They prepare the standard of practices that need to be followed at each unit.
⦁ They can audit and ensure whether each unit is following all the required standards of practices.
⦁ They are responsible for minimizing the environmental impacts due to each unit.
Research Units
Research units are responsible for the innovation of product and production technology. The following are the major responsibilities of Research units.
⦁ Research for the improvement of existing products.
⦁ Research on the diversification of existing products.
⦁ Research for the improvement of existing production technology.
⦁ Development of new technology for production.
⦁ Development of indigenous technologies.
⦁ Development of production technologies suitable for small unit production.
⦁ Adapting state of art technologies into product and production.
⦁ Research for better usage of wastes of production.
⦁ Research to reduce the environmental impacts due to the product and production.
Research needs huge investment, and it will be difficult to arrange such investments at the starting of business. Making collaboration with research teams in Universities, Colleges and Govt Supported industrial institutes could be an economic alternative.
Sales Units
Sales units are responsible for selling the products. They should make use of modern platforms and technologies to sell the products.
Businesses which operate in this model can come together and create an online platform to sell the products.
Marketing Units
Marketing units are responsible for marketing the product. Branding is one of the most important aspects in building trust in the customer and making them buy the products. Building a new brand for each product by different small-scale industries cannot be an affordable strategy for small business units. Bringing all the small-scale industries which follow this model under the same umbrella could save time and effort in marketing. Using the quality and innovation practices mentioned in the model will ensure quality and competitiveness of each product under the brand umbrella.
IT Infrastructure and Coordination Platform Units
Modern IT infrastructure can be used to easily manage and coordinate the geographically distributed units. ERP solutions can be used for better collaboration between units. Open Source technologies can be used wherever possible to reduce the infrastructure expenses. It can provide the technical platform and support for sales and marketing.
Planning, Management and Coordination unit
This unit is responsible for managing the daily operations and coordination between the units. This unit will work closely with the mentoring unit and other units.
⦁ Managing the daily operations.
⦁ Coordination between different units.
⦁ Driving the implementation of plans and strategies prepared by the mentoring unit.
⦁ Getting the feedback and issues from other units and sharing them with the mentoring unit.
⦁ Solving any disputes between different units.
The best practices from both worlds, co-operative, and corporates, can transform small scale industries to a long term competent sustainable business. This approach ensures that the ownership of the business is in the hands of working people while they receive all the modern technology and business strategy support to run the business. A sustainable business model for the small-scale industries can ensure.
⦁ Generation of more jobs.
⦁ Job opportunities for both skilled and unskilled people.
⦁ Development of indigenous technologies.
⦁ Development of technologies suitable for our environment.
⦁ No dependency on corporate and foreign investments.
⦁ Protection of labour rights of the workforce.
⦁ Industries with minimal impact on the environment.
⦁ Helps in the development of the local economy.
⦁ Social and economic empowerment of communities and groups which are part of small-scale industries.